🛡️ Under the Radar: How Modern Hackers Evade Security Systems
Picture this: Right now, as you read these words, invisible digital predators could be lurking inside your network. They’re not setting off alarms. They’re not triggering security alerts. They’re moving like shadows through your systems, stealing data, planting backdoors, and preparing for devastating attacks—all while remaining completely undetected.
In 2024, stealth attacks accounted for over 86% of security breaches in cloud networks. The most dangerous part? These attacks can remain hidden for an average of 287 days before detection. By then, the damage is already done. Ready to meet the invisible enemies that even seasoned security experts struggle to catch?
🎭 Let’s unveil the masters of digital disguise and learn how they operate in the shadows…
👤 Attack Method #1: Social Engineering – The Human Hacking Masterclass
Forget Hollywood scenes of hackers frantically typing code to break through firewalls. The most successful cyber criminals in 2024 are master psychologists who understand that the weakest link isn’t your technology—it’s your people. Social engineering attacks don’t break your systems; they break your trust.
These attacks are devastatingly effective because they bypass all your technical defenses by targeting the one thing you can’t patch: human nature. When someone receives an email that appears to be from their CEO requesting an urgent wire transfer, or a phone call from “IT support” asking for password verification, the natural human response is to help.
🎣 The Modern Phishing Evolution
Today’s phishing attacks have evolved far beyond obvious “Nigerian prince” scams. AI-powered tools now craft personalized messages that perfectly mimic your writing style, reference your recent projects, and even use information gathered from your social media profiles. These spear-phishing attacks are so convincing that they fool executives and IT professionals alike.
🚨 Real-World Example: The $25 Million Deepfake Heist
In early 2024, a finance worker at a multinational firm was tricked into paying $25 million when deepfake technology was used to impersonate the chief financial officer. Every participant in the multi-person video conference was a deepfake. The employee only realized the deception after checking with headquarters.
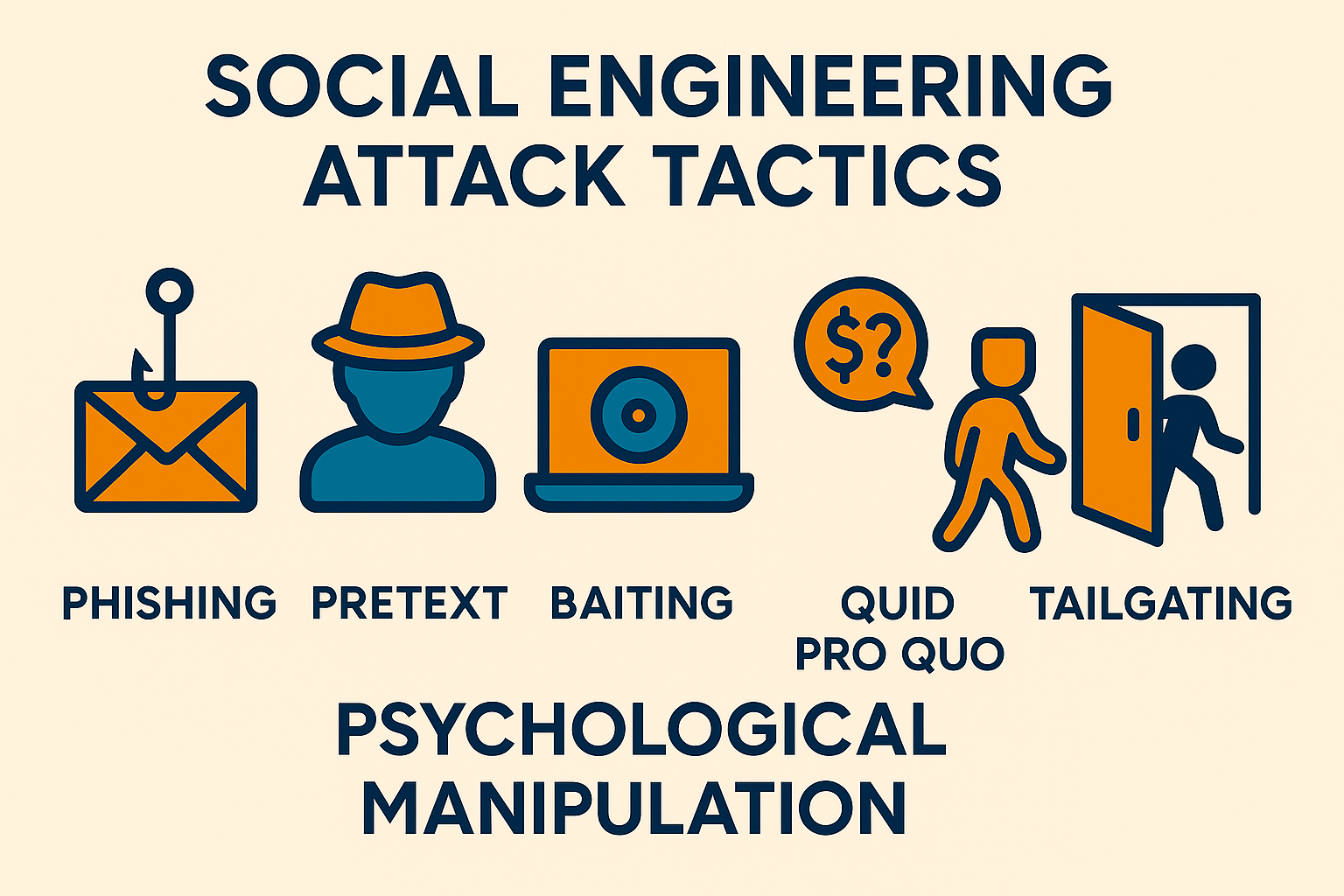
🎪 The Five Faces of Social Engineering
- Pretexting: Creating elaborate fictional scenarios to build trust and extract information
- Baiting: Offering something enticing (like free USB drives) that contains malware
- Quid Pro Quo: Offering a service or benefit in exchange for information or access
- Tailgating: Following authorized personnel into secure areas
- Vishing: Voice phishing using AI-cloned voices of trusted individuals
🔓 While social engineers manipulate minds, our next attacker type exploits the very tools meant to protect us…
🛠️ Attack Method #2: Living Off The Land (LOTL) – Turning Your Tools Against You
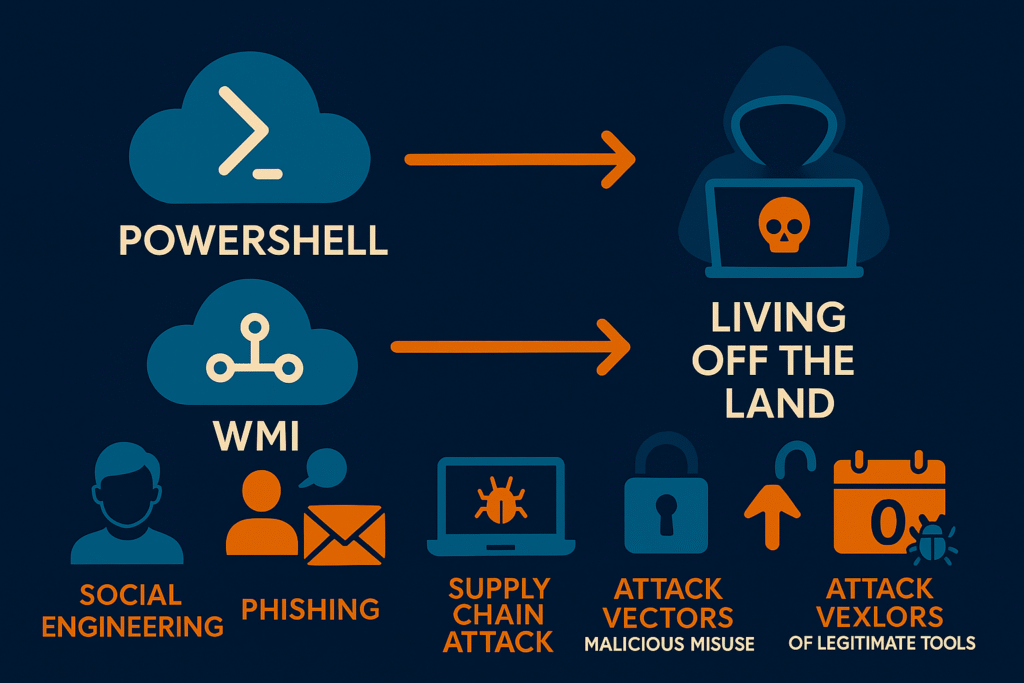
Imagine a burglar who doesn’t bring their own tools but instead uses your hammer, screwdriver, and keys to rob your house. That’s exactly what Living Off The Land attacks do—they weaponize your own legitimate software against you. These attacks are particularly insidious because they blend perfectly with normal system activity.
LOTL attacks use built-in operating system tools like PowerShell, Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), and legitimate administrative utilities to carry out malicious activities. Since these tools are supposed to be there and are regularly used by system administrators, traditional security software often ignores their activities.
📊 LOTL Attack Impact:
According to CrowdStrike’s 2024 Global Threat Report, 62% of attackers now use Living Off The Land techniques. These attacks can remain undetected for months or even years because they generate no traditional malware signatures.
🔧 Common LOTL Tools Weaponized by Attackers
- PowerShell: Microsoft’s powerful scripting language becomes a hacker’s swiss army knife
- WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation): Used for remote system management and data gathering
- PsExec: Legitimate remote execution tool repurposed for lateral movement
- Certutil: Certificate utility abused to download and decode malicious payloads
- Scheduled Tasks: Used to maintain persistence and execute malicious code regularly
⚠️ Why LOTL Attacks Are So Dangerous:
- They leave minimal forensic traces
- Traditional antivirus software can’t detect them
- They operate entirely in memory, making detection extremely difficult
- They appear as normal administrative activities
- They can be automated and scaled across multiple systems
The most sophisticated LOTL attacks combine multiple legitimate tools in sequence, creating complex attack chains that are nearly impossible to distinguish from normal system maintenance. An attacker might use PowerShell to gather system information, WMI to move laterally to other machines, and scheduled tasks to maintain persistent access—all while appearing as routine IT operations.
🕸️ From exploiting trust and tools, we now enter the realm of the most patient and persistent digital predators…
👑 Attack Method #3: Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) – The Digital Ninjas
If cyber attacks were a video game, Advanced Persistent Threats would be the final boss. These are not quick smash-and-grab operations but sophisticated, multi-year campaigns conducted by well-funded groups—often nation-states or organized criminal syndicates. APTs are the digital equivalent of master spies who infiltrate enemy territory and remain undetected for years.
What makes APTs particularly terrifying is their patience and precision. While other attackers rush to monetize their access, APT groups play the long game. They establish multiple entry points, create redundant access methods, and carefully study their targets before making any moves that might alert security teams.
🎯 The APT Attack Lifecycle
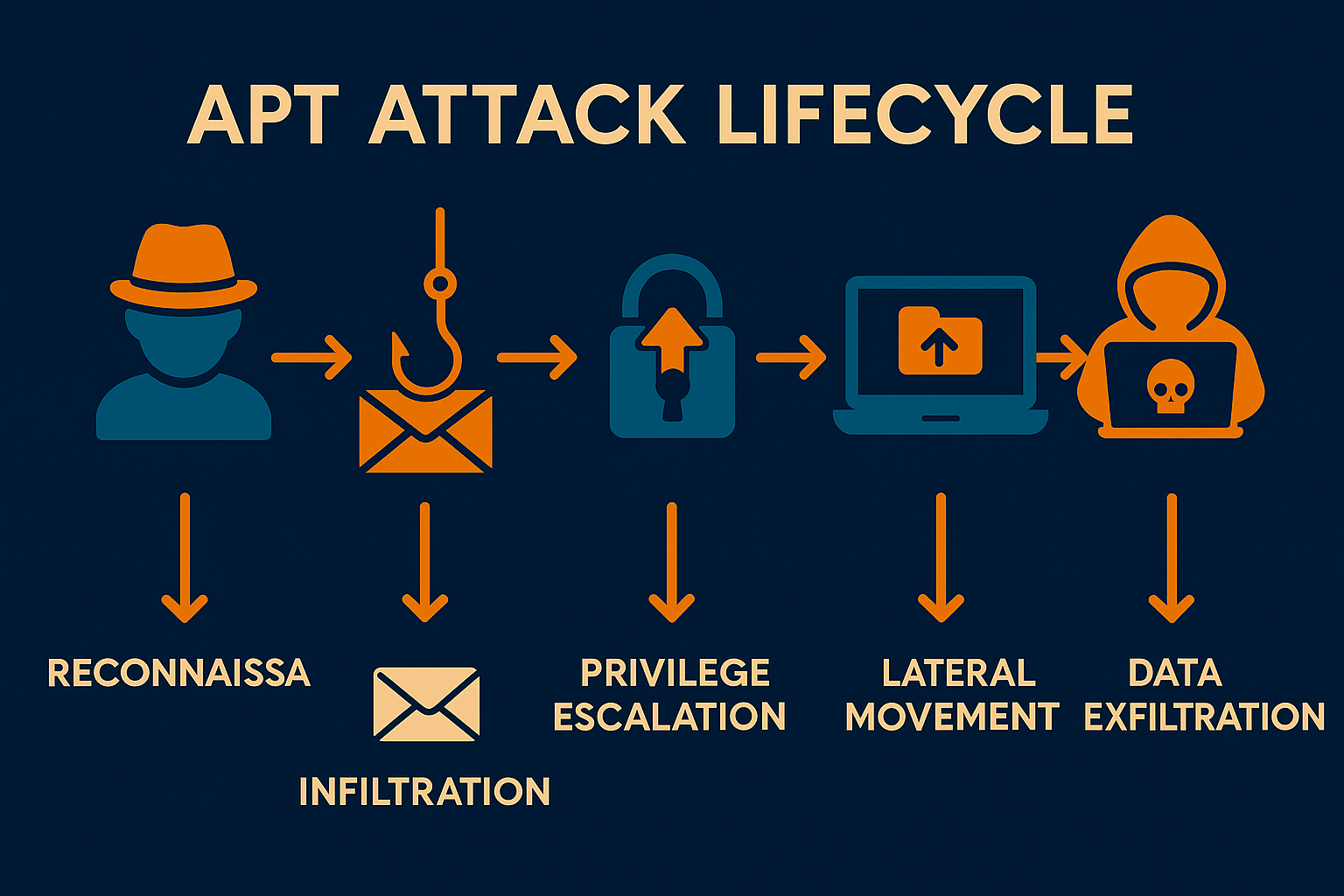
APT attacks follow a methodical approach that can span months or years:
- Reconnaissance: Extensive research on targets, employees, infrastructure, and vulnerabilities
- Initial Infiltration: Gaining first foothold through spear-phishing, zero-days, or supply chain compromise
- Establishing Persistence: Creating multiple backdoors and hidden access points
- Privilege Escalation: Gradually gaining higher-level access throughout the network
- Lateral Movement: Spreading silently across systems to map the entire environment
- Data Collection: Identifying and cataloging valuable information assets
- Exfiltration: Slowly extracting data over extended periods to avoid detection
🌐 Real-World APT Example: Volt Typhoon
This Chinese state-sponsored APT group has been infiltrating U.S. critical infrastructure since 2021. They specialize in “living off the land” techniques and focus on operational technology assets. Volt Typhoon avoids using compromised credentials during non-working hours to evade detection and has successfully maintained access to multiple organizations for years without being discovered.
🛡️ APT Evasion Techniques
- Operational Security: Mimicking normal user behavior and working hours
- Encrypted Communications: Using legitimate communication channels for command and control
- Custom Malware: Developing unique tools that signature-based detection can’t identify
- Supply Chain Infiltration: Compromising trusted software vendors to reach multiple targets
- Zero-Day Exploits: Using unknown vulnerabilities that have no available patches
⚡ Speaking of zero-days, let’s explore these mysterious vulnerabilities that even security experts fear…
🔍 Attack Method #4: Zero-Day Exploits – The Unknown Unknowns
Zero-day exploits are the stuff of cybersecurity nightmares. These attacks leverage vulnerabilities that are completely unknown to software vendors, security researchers, and IT teams. The name “zero-day” refers to the fact that developers have had zero days to create and distribute a fix for the vulnerability.
What makes zero-day attacks particularly insidious is their element of complete surprise. Traditional security defenses rely on knowing what to look for—specific malware signatures, attack patterns, or vulnerability indicators. Zero-day attacks, by definition, have none of these known characteristics.
💰 The Zero-Day Economy
Zero-day vulnerabilities have become valuable commodities in underground markets. Sophisticated exploit brokers now operate like legitimate businesses, complete with customer service and quality guarantees. A single zero-day exploit can sell for anywhere from $100,000 to several million dollars, depending on the target software and potential impact.
📈 Zero-Day Explosion:
A 2024 Mandiant report found that more zero-day vulnerabilities were exploited in 2023 alone than in all of 2020-2022 combined. The rise is attributed to increasing network complexity and the expansion of attack surfaces through cloud adoption and IoT devices.
🎭 Notable Zero-Day Attacks That Shook the World
- Stuxnet (2010): Used four different zero-days to target Iranian nuclear facilities
- Log4Shell (2021): A vulnerability in a widely-used Java library that affected millions of devices
- MOVEit Zero-Day (2023): Compromised hundreds of organizations through file transfer software
- Chrome Zero-Days (2024): Multiple browser vulnerabilities exploited by North Korean hackers
🚨 Why Zero-Day Attacks Are Unstoppable:
- No patches or fixes exist when the attack occurs
- Security software has no signatures to detect them
- Attackers can exploit them for months before discovery
- Nation-state actors often stockpile zero-days for strategic use
- The vulnerability window can last from days to years
The most dangerous aspect of zero-day attacks is their potential for widespread impact. When a zero-day affects popular software like web browsers, operating systems, or widely-used applications, millions of users can be vulnerable simultaneously. The 2021 Log4Shell vulnerability, for example, affected popular programs like Apple iCloud and Minecraft, putting hundreds of millions of devices at risk.
🔗 Our final attack method shows how one compromise can create a domino effect across entire industries…
⛓️ Attack Method #5: Supply Chain Attacks – The Trojan Horse Strategy
Supply chain attacks represent the ultimate expression of the phrase “it’s not what you know, it’s who you trust.” These attacks don’t target you directly—they target the vendors, partners, and service providers you rely on. By compromising a trusted third party, attackers can simultaneously breach hundreds or even thousands of organizations through a single point of failure.
The beauty of supply chain attacks, from an attacker’s perspective, is their incredible efficiency. Why break into 1,000 companies individually when you can compromise their shared software vendor and access all of them at once? This multiplication effect makes supply chain attacks one of the most devastating and scalable attack methods available.
🎯 Types of Supply Chain Compromise
- Software Supply Chain: Injecting malicious code into legitimate software updates
- Hardware Supply Chain: Compromising devices during manufacturing or shipping
- Service Provider Attacks: Targeting managed service providers to reach their clients
- Open Source Poisoning: Inserting malicious code into popular open-source libraries
💥 The 2024 Supply Chain Attack Wave:
Change Healthcare: A ransomware attack on this major health payment processor disrupted operations and exposed 6TB of patient data, costing the company $2.3 billion and affecting healthcare providers nationwide.
CrowdStrike Global Outage: A faulty software update caused one of the largest IT outages in history, affecting 8.5 million systems worldwide and demonstrating how even cybersecurity companies can become supply chain vulnerabilities.
🌊 The Ripple Effect
What makes supply chain attacks particularly devastating is their cascading impact. When Change Healthcare was compromised in 2024, it didn’t just affect one company—it disrupted healthcare operations across three states, causing delayed lab results, medication errors, and the absence of routine safety checks that prevent potentially fatal mistakes.
📊 Supply Chain Attack Growth:
Software supply chain attacks increased by 25% from 2023 to 2024, with the last two months of the reporting period showing nearly double the attack frequency. These attacks now affect an average of 16 organizations per month compared to 13 in the previous period.
🔍 How Supply Chain Attacks Stay Hidden
Supply chain attacks are masters of disguise because they arrive through trusted channels. When your antivirus software receives an update, your firewall gets a patch, or your favorite application downloads an enhancement, your security systems don’t scrutinize these activities—they’re supposed to happen. This trust relationship is exactly what attackers exploit.
- Legitimate Code Signing: Malicious updates are signed with valid certificates
- Trusted Delivery Channels: Attacks arrive through official update mechanisms
- Delayed Activation: Malicious code may remain dormant for months before activating
- Minimal Footprint: Only small portions of code are modified to avoid detection
🎬 Now that we’ve met these invisible enemies, let’s understand why traditional security measures often fail to stop them…
🚫 Why Traditional Security Fails Against Stealth Attacks
Traditional cybersecurity operates on a simple premise: build walls, set up alarms, and watch for known bad actors. This approach worked well when attacks were obvious, noisy, and used recognizable patterns. But stealth attacks have fundamentally changed the game by exploiting the blind spots in traditional security models.
🔧 The Traditional Security Mindset
Most security systems are designed to catch what they recognize. They maintain databases of malware signatures, lists of malicious IP addresses, and patterns of suspicious behavior. When something matches these known indicators, alarms sound. The problem? Stealth attacks are specifically designed to avoid matching these patterns.
🚨 Critical Security Blind Spots:
- Trust Assumptions: Security systems trust legitimate tools and signed software
- Signature Dependence: Unknown threats leave no signatures to detect
- Behavioral Blindness: Gradual, patient attacks don’t trigger behavioral alarms
- Human Factor Ignorance: Technical solutions can’t address social engineering
- Supply Chain Trust: Updates and patches from trusted vendors aren’t scrutinized
⚡ The Speed vs. Stealth Paradox
Traditional security systems are optimized to catch fast, obvious attacks. They excel at stopping automated malware that spreads rapidly and triggers multiple alerts. However, this optimization creates a blind spot for slow, methodical attacks that unfold over months or years.
“The most dangerous attacks today don’t look like attacks at all. They look like legitimate business activity, normal system administration, and trusted software updates. This is why 86% of security breaches now involve stealth techniques.”
— Cybersecurity Expert, 2024
💡 Understanding these attacks is the first step. In our next article, we’ll explore exactly how to build defenses that can catch even the most invisible enemies…
🎯 The Stealth Attack Playbook: Common Patterns
While each stealth attack method has unique characteristics, successful attacks often follow similar patterns. Understanding these patterns can help security teams identify threats even when specific indicators aren’t available.
📋 The Universal Stealth Attack Sequence
- Reconnaissance Phase: Extensive research using open-source intelligence
- Initial Access: Gaining foothold through social engineering or trusted channels
- Environment Mapping: Quietly exploring the network to understand its structure
- Privilege Collection: Gradually accumulating higher-level access rights
- Persistence Establishment: Creating multiple hidden access points
- Objective Achievement: Executing the ultimate goal (data theft, sabotage, etc.)
- Cover-Up Activities: Removing traces and maintaining ongoing access
🕰️ The Dwell Time Challenge
One of the most alarming aspects of stealth attacks is their extended dwell time—the period between initial compromise and detection. In 2024, the average dwell time for stealth attacks was 287 days, with some APT groups maintaining access for over three years before discovery.
⏰ Dwell Time by Attack Type:
- Social Engineering: 21 days average detection time
- Living Off The Land: 195 days average detection time
- APT Attacks: 287 days average detection time
- Zero-Day Exploits: 14 days (after vulnerability disclosure)
- Supply Chain: 156 days average detection time
🚀 The landscape of stealth attacks continues to evolve. Let’s examine what’s coming next…
🔮 The Evolution of Stealth Attacks: What’s Coming in 2025
As we move deeper into 2025, stealth attacks are becoming even more sophisticated. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation are being weaponized by attackers to create threats that adapt, evolve, and learn from defensive responses.
🤖 AI-Powered Attack Evolution
- Autonomous Attack Systems: AI agents that can conduct entire attack campaigns without human intervention
- Dynamic Payload Generation: Malware that rewrites itself to evade detection
- Behavioral Mimicry: Attacks that learn normal user patterns and perfectly imitate them
- Real-Time Social Engineering: AI chatbots that conduct convincing live conversations with targets
- Predictive Targeting: Systems that identify the most vulnerable targets before launching attacks
🌐 The Expanding Attack Surface
The proliferation of cloud services, IoT devices, and remote work has created an exponentially larger attack surface. Each new technology represents potential new hiding places for stealth attacks. 5G networks, edge computing, and quantum communications all introduce novel opportunities for invisible infiltration.
🎯 Emerging Threat: AI-Enhanced APTs
Security researchers are already observing APT groups experimenting with AI tools to enhance their social engineering campaigns, automate reconnaissance activities, and create more convincing deepfakes. These AI-enhanced attacks could reduce the skill level required for sophisticated campaigns while dramatically increasing their success rates.
⚔️ The battle between attackers and defenders continues to escalate, but knowledge is our greatest weapon…
🧠 The Psychology of Invisible Attacks
Understanding stealth attacks isn’t just about technology—it’s about psychology. Both attackers and defenders operate within psychological frameworks that influence their decision-making, risk assessment, and response strategies.
🎭 The Attacker’s Mindset
Stealth attackers think like intelligence operatives. They prioritize patience over speed, precision over volume, and sustainability over immediate gratification. This mindset shift represents a fundamental evolution in cybercrime from smash-and-grab operations to long-term strategic campaigns.
🛡️ The Defender’s Dilemma
Defenders face an inherent psychological challenge: they must simultaneously protect against known threats while remaining vigilant for unknown ones. This cognitive burden often leads to alert fatigue, over-reliance on automated systems, and blind spots in threat detection.
🧠 Psychological Factors That Enable Stealth Attacks:
- Normalization: Gradual attacks blend into routine activities
- Trust Exploitation: Leveraging established trust relationships
- Attention Overload: Defenders become overwhelmed by security alerts
- Confirmation Bias: Looking for expected threats while missing novel ones
- Automation Dependency: Over-reliance on systems that miss human-targeted attacks
🎊 Armed with this knowledge, we’re ready to explore how to build defenses against these invisible enemies…
🎯 Key Takeaways: Recognizing the Invisible Enemy
The five stealth attack methods we’ve explored represent the evolution of cyber warfare from noisy, obvious assaults to sophisticated, invisible infiltrations. Each method exploits different aspects of our digital trust relationships and security assumptions.
🔑 Critical Defense Principles:
- Assume Breach: Operate under the assumption that attackers are already inside your network
- Trust but Verify: Implement continuous verification for all users, devices, and activities
- Behavioral Analytics: Focus on detecting anomalous patterns rather than known signatures
- Human Factor Security: Address social engineering through training and culture
- Supply Chain Vigilance: Scrutinize trusted vendors and partners as potential attack vectors
🚨 Warning Signs of Stealth Attacks
While stealth attacks are designed to be invisible, they often leave subtle traces that trained observers can detect:
- Unusual Administrative Activity: Legitimate tools used at odd hours or by unexpected users
- Gradual Privilege Creep: Users slowly accumulating access rights over time
- Anomalous Data Flows: Small but consistent data transfers to unusual destinations
- Behavioral Changes: Employees exhibiting different digital behavior patterns
- Performance Degradation: Subtle system slowdowns that might indicate hidden activities
The invisible nature of these attacks doesn’t make them unstoppable—it simply requires a different approach to detection and defense. Traditional perimeter security must evolve into comprehensive, behavior-based protection that assumes attackers are already inside and focuses on limiting their movement and impact.
🌟 Ready to turn the tables on these invisible enemies? Our next article will reveal the advanced defense strategies that can catch even the stealthiest attackers…
🎉 Your Journey Into the Shadows
You’ve now glimpsed into the shadowy world of stealth cyber attacks—the invisible enemies that slip past traditional defenses and operate in the darkness of our digital infrastructure. From social engineers who hack human psychology to APT groups that play the long game across years, these threats represent the cutting edge of cyber warfare.
Understanding these attack methods isn’t just academic knowledge—it’s essential survival information for anyone responsible for digital security in 2025. As attacks become more sophisticated and invisible, the gap between those who understand these threats and those who don’t will determine who survives in cyberspace.
🚀 Coming Next: Building Unbreachable Defenses
In our follow-up article, “Fortress Mode: How to Build Infrastructure That Stops Even Invisible Attacks,” we’ll explore:
- Zero Trust Architecture: Never trust, always verify—even your own systems
- Behavioral Analytics: AI-powered systems that detect anomalies humans miss
- Deception Technology: Setting traps that catch stealth attackers
- Supply Chain Security: Protecting your trusted relationships
- Human Firewall Training: Turning your people into your strongest defense
The cybersecurity landscape has fundamentally changed. The days of relying solely on perimeter defenses and signature-based detection are over. The future belongs to organizations that understand the invisible enemy and build defenses designed for the shadows.
Remember: These attacks succeed not because they’re technically superior, but because they exploit our assumptions about trust, legitimacy, and normal behavior. By understanding their methods, we can begin to see through their invisibility cloak and build defenses that protect against what we can’t see.
🔍 Stay vigilant, stay curious, and remember: In cybersecurity, what you can’t see can definitely hurt you—but knowledge is your best defense against the invisible enemy!
The shadows may hide our enemies, but they can’t hide from informed defenders. Your journey into advanced cybersecurity defense starts now! 🛡️✨
